- Small
- Large
Information Disclosure Based on TCFD Recommendations
The LINTEC Group recognizes that climate change has impacts on its business activities and positions it as an important management issue. We will strengthen our risk management system and responses to risks and find new business opportunities to make contributions for our sustainable growth and the development of a sustainable society. Moreover, we will proactively disclose information on our responses to climate change according to the recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) and further improve our corporate value through engagement with stakeholders.
Governance
The Sustainability Committee (meeting four times a year, in principle) discusses policies and implementation plans and supervises their progress regarding specific measures related to sustainability, including responses to climate change-related issues. The committee is chaired by the president and comprised of all directors and officers in charge of promoting committees under the Sustainability Committee. The outcomes of discussions are reported to the Board of Directors.
Climate change-related issues are assessed firstly by the Environmental Committee, via the TCFD Subcommittee, and finally by the Sustainability Committee. Measures to respond to issues are implemented and managed at each site. The status of responses is put together by the Environmental Committee and reported to all directors and officers in charge at the Sustainability Committee.
Strategy
Considering risks and opportunities associated with climate change as an important matter in developing its business strategies, the LINTEC Group set out the following two scenarios and conducted scenario analysis for its domestic business up to 2030(medium-term) and 2050 (long-term). Consequently, we identified risks and opportunities, as shown in the following table.
We will integrate measures to respond to these climate change-related risks and opportunities into initiatives we take under our long-term vision, LSV 2030, and will carry out analysis, covering our business outside Japan, from a longer-term perspective.
Slide to view.
| +4°C scenario | +2°C or below 1.5°C scenario | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Reference Scenario | Transition Risks | Transition scenario, International Energy Agency (IEA) | |
| Stated Policies Scenario (STEPS)★1 | Sustainable Development Scenario (SDS) Net Zero Emissions by 2050 (NZE)★1 |
||
| Physical Risks | Climate change scenario, Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) | ||
| RCP 8.5★2 | RCP 2.6★2 | ||
| Technology Roadmap for Transition Finance formulated by the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry | |||
| Image of society that LINTEC envisions |
[Society where policies continue as they are and climate change progresses]
|
[Society where active measures are taken toward realizing a carbon-free world]
|
|
- ★1Source: IEA. World Energy Outlook 2021, World Energy Outlook 2022
- ★2Source: IPCC. Fifth Assessment Report
- ★3ZEB (Net Zero Energy Building) and ZEH (Net Zero Energy House) refer to buildings and houses with an annual energy consumption that is effectively zero or less, which is achieved by installing equipment such as high-insulation, highly airtight, highly efficient equipment and solar power systems.
Scope
The scope of this scenario analysis only includes our business in Japan. We will consider expanding the scope to include our overseas business in scenario analyses to be conducted in the future.
Timeline
“Medium-term” refers to the period up to 2030, which is the final year of the LINTEC Group’s long-term vision and SDGs. “Long-term” refers to the period up to 2050, which is the Group’s target year for achieving carbon neutrality. For future financial impact, the analysis was conducted by focusing on 2030.
World of +2°C or Less
Transition Risks
Slide to view.
| Category | Major risks | Timeline | Proposed responses | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Policy and legal | Carbon pricing | Decline in price competitiveness due to the increased cost needed to respond to tougher laws and regulations on GHG emissions and energy usage (such as introduction of a carbon tax), as well as higher manufacturing cost and price pass-through | Medium- to long-term |
|
| Tightened regulation of CO2 emissions | Investment unrecovered due to increased capital investment for saving energy and reducing CO2 emissions | Medium- to long-term |
|
|
| Increased burden in order to respond to more sophisticated disclosure of information on GHG emissions and the obligation to disclose such information | Medium- to long-term |
|
||
| Tightened regulations on VOC emissions | Decline in sales of solvent products and changes in specifications | Medium- to long-term |
|
|
| Technology | Development of new technologies | Loss of business opportunities if development of products that address climate change is delayed, or if existing products cannot meet environmental needs. | Medium- to long-term |
|
| Decline in competitiveness due to delays in research and development of new technologies, securing intellectual property rights, or joint development efforts, etc. | Medium- to long-term |
|
||
| Market | Changing energy costs | Increased manufacturing costs and utility costs due to rising prices of crude oil- and petroleum-based energy | Medium-term |
|
| Changing important products | Decrease in orders received for our core products as customer needs shift toward environmentally friendly products | Medium- to long-term |
|
|
| Changing raw material procurement | Unstable product supply due to increased dependence on suppliers as a result of accelerated conversion to non-petrochemical raw materials | Medium- to long-term |
|
|
| Increase in the cost of raw materials due to measures taken by suppliers to reduce CO2 emissions | Medium- to long-term |
|
||
| Reputation | Changing reputation among customers | Decline in customer ratings and decrease in sales due to delays in establishing systems to tackle climate change and in deploying and enhancing products that address climate change | Medium- to long-term |
|
Opportunities
Slide to view.
| Category | Major risks | Timeline | Proposed responses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resource efficiency | Reduction in cost for water supply and effluent through recycling water | Medium- to long-term |
|
| Effective capital investments in new equipment through adoption of internal carbon pricing | Medium-term |
|
|
| Energy sources | Promotion of cost reduction in energy procurement | Medium- to long-term |
|
| Monetization of emissions trading by keeping CO2 emissions within emissions allowances | Medium- to long-term |
|
|
| Adoption of alternative energy for carbon-free | Long-term |
|
|
| Increase in opportunities to procure materials that are manufactured with energy sources and/or raw materials made available through innovation by suppliers, which contribute toward achieving carbon neutrality | Medium- to long-term |
|
|
| Products and services | Increase in demand for electronics-related products due to acceleration of digitalization and popularization of EV | Medium- to long-term |
|
| Increase in needs for products and initiatives that contribute to the realization of a circular society | Medium- to long-term |
|
|
| Increase in business opportunities owing to popularization and expansion of renewable energy | Medium- to long-term |
|
|
| Increase in opportunities to sell energy-efficient products | Medium- to long-term |
|
|
| Increase in opportunities to sell solvent-free products | Medium- to long-term |
|
|
| Acquisition of new business opportunities owing to the increased environmental awareness of employees | Medium- to long-term |
|
|
| Market | Gaining support of stakeholders by enhancing initiatives for realizing a carbon-free world and a circular society | Medium- to long-term |
|
| Resilience | Stabilizing supply chains by reviewing suppliers | Medium- to long-term |
|
World of +4°C
Physical risks
Slide to view.
| Category | Major risks | Timeline | Proposed responses | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acute | Exacerbation of natural disasters | Delay in supplying products due to a supply chain disruption and/or shutdown of a plant due to torrential rain, resulting in a drop in sales | Medium- to long-term |
|
| Increase in repair cost and accident and disaster insurance cost | Medium- to long-term |
|
||
| Chronic | Rise in temperatures | Increase in air conditioning cost during the summer | Medium- to long-term |
|
| Instability in securing water | Shortage of industrial water due to a decrease in groundwater | Medium- to long-term |
|
|
- ★BCP: BCP stands for a Business Continuity Plan. It is a plan developed in advance to enable the minimization of damage and the continuation or early resumption of business in the event that a company encounters an emergency situation such as an accident or disaster.
Financial Impact of Risks and Opportunities Related to Climate Change
Financial impact of transition risks
- Increase in cost due to carbon pricing
We aim to reduce CO2 emissions by 50% or more by 2030 compared to fiscal 2013 levels, and achieve net zero by 2050. If a carbon tax is introduced, the estimated carbon tax burden incurred by the company will be approximately 2 billion yen if the company achieves the goal in 2030. This is approximately 1.1 billion yen less than the cost that would be incurred if the company does not work on reducing CO2 emissions. - Capital investments to reduce CO2 emissions
We plan to invest approximately 14.7 billion yen in total to reduce CO2 emissions in Japan during the period of our long-term vision, “LSV 2030,” by adopting solar power generation systems for captive consumption and gas turbine cogeneration systems. - Changes in the raw material procurement environment
Some of our products use fossil fuels and raw materials derived from pulp. Consequently, we recognize that our business faces high long-term risk derived from changes in the raw material procurement environment. We will continue to analyze the degree of impact and consider countermeasures, such as switching raw materials and adopting new technologies.
Financial impact of physical risks
- Torrential rain and floods
We will minimize the impact and ensure a stable supply of products by purchasing raw materials from multiple suppliers, maintaining an adequate level of inventory at each site, and establishing back-up systems through BCP★. - ★BCP: BCP stands for a Business Continuity Plan. It is a plan developed in advance to enable the minimization of damage and the continuation or early resumption of business in the event that a company encounters an emergency situation such as an accident or disaster.
- Droughts
We will minimize the impact by making continuous efforts to develop multiple industrial water systems and reduce industrial water usage at each site.
Financial impact of opportunities
- Increase in demand for various types of environmentally friendly products
As companies promote countermeasures against global warming and consumer attitudes shift toward environment-conscious and sustainable living, demand for our environmentally friendly products is expected to increase. We are currently calculating the amount of financial impact. - Increase in demand for energy-efficient products
With growing needs for energy conservation and disaster prevention as well as the advancement of industrialization and urbanization in emerging countries, demand for our energy-efficient products is expected to increase. We are currently calculating the amount of financial impact.
Results of Our Scenario Analysis
As a result of our scenario analysis, we confirmed that both scenarios we examined will have a certain degree of impact on our business in 2030 and 2050, such as the impact of increased raw materials costs, and the impact on demand for energy-efficient products related to our initiatives under the long-term vision of “LSV 2030” as well as various types of environmentally friendly products. Consequently, we reconfirmed the need for actively working on managing risks and capturing opportunities. We will continue to take necessary measures as a group-wide effort, and actively work on reducing CO2 emissions by 50% or more by 2030 compared to fiscal 2013 levels and achieving net zero by 2050.
Initiatives of the LINTEC Group
Risk Management
In April 2018, the LINTEC Group established a Corporate Risk Management Committee comprised of executive general managers and general managers from offices under the direct control of the president with the aim of enhancing its risk management systems, and the committee periodically holds meetings.
In April 2021, the system for promoting sustainability activities was renewed and strengthened, and the purpose of this Committee was redefined as “identifying risks and opportunities in business operation; formulating policies to manage them; and planning and verifying worksite-level measures.” The committee assesses and analyzes various risks, including those related to natural disasters, based on the issues recognized by committee members and the results of the annual risk identification process for managers. The results are reported to the Sustainability Committee every quarter, who then gives instructions on response measures.
In addition, information related to climate-related risks is gathered and identified/assessed by the Environmental Committee, and the results are reported to the Sustainability Committee. The Sustainability Committee considers whether any response measures need to be implemented, and then provides instructions to officers in charge of promotion through subcommittees as needed. Officers who receive instructions then implement measures through departments for which they are responsible. The Environmental Committee monitors subsequent changes in circumstances on an ongoing basis, and periodically checks whether initial indicators/ goals have been achieved.
These committees will continue to work together to strengthen our risk management capabilities and enhance our risk management systems to contribute to the sustainable growth of the LINTEC Group.
Related Information
Metrics and Targets
The LINTEC Group recognizes that reduction of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions is crucial in addressing climate change and accordingly promotes various measures in R&D, manufacturing, sales, and logistics. As a manufacturer, LINTEC views these initiatives for carbon-free as its mission and as leading to new climate-related opportunities. In its long-term vision toward 2030, “LSV 2030,” the LINTEC Group has set the following numerical target.
Target
Reduce CO2 emissions by 50% or more by 2030 compared to fiscal 2013 levels, and achieve net zero by 2050.
Results
Amount of CO2 emissions
Organizations covered: LINTEC CORPORATION’s Head Office, 10 production sites★, the Research Center, sales offices, the Osaka Distribution Center, TOKYO LINTEC KAKO, INC., and SHONAN LINTEC KAKO, INC. (the scope for which regular reporting under the Energy Conservation Act is required)
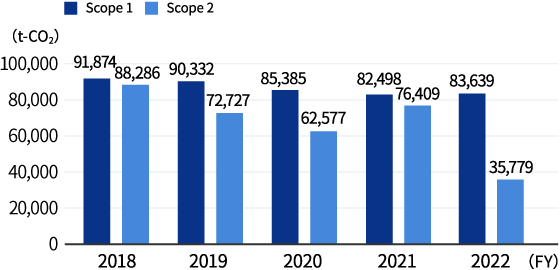
- ★10 production sites: Agatsuma, Kumagaya, Ina, Chiba, Tatsuno, Shingu, Komatsushima, Mishima, Doi, and Niihama
Goals and indicators are also listed in the below:
- Message from the President
- Concept and Systems
- Highlight: Initiatives for the Reduction of CO2 Emissions
- Environmental Report
- Environmental Management System
- Developing Environmentally Friendly Products
- Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation
- Realization of a Recycling-oriented Society
- Co-existence with Nature
- Management of Environmentally Hazardous Substances
- Environmental Accounting
- Environmental Data of Group Companies Outside Japan
- Relationship between LINTEC and the Environment
- Social Report
- Providing Value to Customers
- Cooperating with Suppliers
- Together with Employees (Human Rights / Employment)
- Together with Employees (Human Resource Development)
- Together with Employees (Safety and Disaster Prevention)
- Together with Local Communities
- Together with Shareholders
- Communicating with Stakeholders
- Governance Report
- SDGs-related Initiatives
- CSR Activities at Group Companies Inside and Outside of Japan
- Information Disclosure Based on TCFD Recommendations
- Corporate Policies
- Reporting Policy
- Performance Data
- GRI Index
- Message from Outside Director
- Third-Party Verification
- External Evaluations
- Download Report

